SUBJECTS-
1 Schools closed
2 Risk Control
3 Time
4 Background
4.1 Shutdown nationwide
4.2 Localized closure
5 School closure results
5.1 Stress on the health care system
5.2 Distance education
5.3 Caring for children
5.4 Nutrition and food insecurity
5.5 Student Learning Outcomes
5.6 Access to mitigation strategies
5.7 Special education services
5.8 Effect of school closure on COVID-19 cases and deaths
Impact on formal school education
6.1 Early childhood education
6.2 Basic
6.3 Secondary
6.4 grade per inflation
6.5 Tertiary (Higher)
7 Answers to the crisiS.
7.1 UNESCO Recommendations
7.2 Open Education Community Feedback
Background Further information:
- Effect of COVID-19 infection on Children and youth drop out of faculty because of the closure of COVID-19 and therefore the classification of kids as NEET Attempts to stop the spread of non-drug interventions and preventive measures like COVID-19 on social-discrimination and self-isolation have led to the widespread closure of primary, secondary and tertiary schools in additional than 100 countries.
- The prevalence of previous infectious diseases has led to widespread school closures worldwide, at various levels. The closure of math modeling schools has been shown to delay transmission.
- However, the impact will rely on the contacts the kids maintain outside of college. the college dropouts appear to be effective in reducing cases and deaths, especially when implemented immediately.
- If school interruptions are delayed thanks to outbreaks, they will be less effective and should not be effective. additionally, in some cases, reopening schools after the closure period has increased the infection rate.
- When other public interventions, like the ban on public meetings, begin to be banned, it’s difficult to quantify the particular impact of faculty closures. Influenza infections, school closures, and public collection restrictions were related to a lower deathrate within the u. s. between 1918 and 1919.
- Cities that had previously implemented such interventions were more likely to delay reaching maximum mortality. in line with a study of the response of 43 U.S. cities to the Spanish flu, schools were closed for a median of 4 weeks. .
- School closures within the Japanese city of Oita have successfully reduced the quantity of infected students; However, the closure of faculties failed to reduce the whole number of infected students.
- Compulsory school closures and other social distance measures are related to reducing the influenza transmission rate from 29% to 37%. Early school closures within the U.S delayed the height of the 2009 H1N1
- Especially among doctors and nurses with a high percentage of ladies. , 1/2 them women. There are children under 16 years old. He also examined the dynamics of the spread of influenza in France during the French school holidays and located that flu cases decreased when schools reopened and re-emerged after they reopened.
- He noted that when teachers went on strike in Israel during the 1999-2000 flu season, the amount of visiting doctors and respiratory infections dropped by a fifth and two-fifths, respectively. Bullying controls More info: Office Risk Control for COVID-19 For schools and childcare facilities, U.S.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends short-term closure to scrub or disinfect an infected person living during a pseudo.
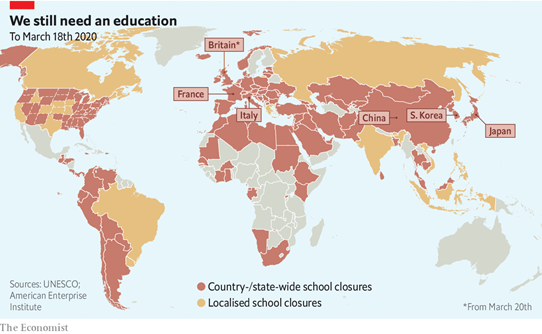
The School is Closed: Countrywide Closure
Ambox is currently Red Asia Australia. Svg
This section needs to be updated. Please update this article to reflect recent events or new information available. (May 2020)
Data on school closures nationwide by country/region
Country and Region, Number of Practitioners in Pre-Primary to Higher Secondary Education Number of Practitioners in Tertiary Education Program Additional Information
1.) 9,608,795 370,610 COVID-19 pandemic in Afghanistan
2.) Albania 520,759 131,833 schools closed for two weeks. The COVID-19 pandemic in Albania
3.) 9,492,542 743,640 COVID-19 infections in Algeria
4.) Argentina 11,061,186 3,140,963 COVID-19 pandemic in Argentina
5.) 437,612 102,891 COVID-19 epidemic in Armenia
6.) Austria G 1,278,170 430,370 schools closed. The COVID-19 pandemic in Austria
7.) 1,783,390 200,609 COVID-19 infections in Azerbaijan
8.) 247,489 44,940 COVID-19 epidemic in Bahrain
9.) 36,786,304 3,150,539 schools in Bangladesh closed COVID-19 pandemic
10.) Belgium 2,457,738 526,720 Nurseries remain open despite closed schools. COVID-19 pandemic in Belgium
11.) 176,488 11,944 COVID-19 epidemics in Bhutan
12.) 612,837 – COVID-19 pandemic in Bolivia
13.) Bosnia and Herzegovina 428,099 95,142 schools and universities were closed. COVID-19 pandemic in Bosnia and Herzegovina
14.) Bulgaria 974,469 249,937 schools and universities closed. COVID-19 pandemic in Bulgaria
15.) Burkina Faso 4,568,998 117,725 Burkina Faso closed all preschool, elementary, post-primary, and secondary, vocational, and university institutions from March 16 to 31. COVID-19 pandemic in Burkina Faso
16.) Canada 25,017,635 1,625,578 On March 16, all schools except British Columbia and the Yukon were closed at the regional and regional levels. However, Yukon schools began the spring break on March 16 and extended the bandh from March 18, 2020 to April 15, 2020. K-12 schools in British Columbia were closed indefinitely on March 17. All educational institutions were closed by the end of March. The COVID-19 pandemic in Canada
17.) 3,310,778 211,484 COVID-19 infections in Cambodia
18.) Cayman Islands 9,182 – A COVID-19 pandemic in the Cayman Islands
19.) Chile 3,652,100 1,238,992 Chilean President Sebastian Pinera has announced that schools across the country will be closed only when a coronavirus case is confirmed among students. COVID-19 pandemic in Chile
20.) China (including Hong Kong and Macau) was the first country to order school closures due to the B233,169,621 42,266,464 virus. Following the Spring Festival holiday, China has asked its nearly 200 million students to stay home and continue their education online. According to UNESCO, China began reopening schools by March 13, although the majority closed. The COVID-19 pandemic in mainland China
21.) 9,124,862 2,408,041 COVID-19 infections in Colombia
22.) 1,100,782 216,700 COVID-19 epidemic in Costa Rica
23.) Croatia 621,991 165,197 Both schools and universities were closed. COVID-19 pandemic in Croatia
24.) COVID-19 epidemics in Cyprus Czech Republic 1,715,890 352,873 schools and universities closed. COVID-19 pandemic in the Czech Republic
25.) Democratic People’s Republic of Korea 4,229,170 526,400 COVID-19 pandemic
26.) Denmark 1,185,564 312,379 Both schools and universities were closed. The COVID-19 pandemic in Denmark
Consequences
- School closures in response to the COVID-19 epidemic have affected access to education, as well as a wide range of socio-economic issues.
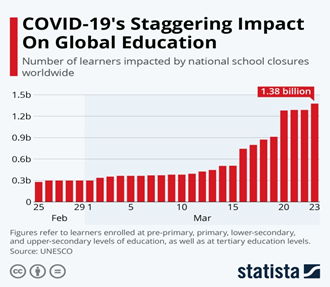
- More than 370 million children and youth are out of school as of March 12 due to government temporary or indefinite school closures n an effort to slow the spread of COVID-19.
- As of March 29, 90% of practitioners worldwide were affected by the closure.
- Although school closures are temporary, it can have high social and economic costs.
- They cause disruptions that affect people in communities, but their effects are more severe for underprivileged children and their families, including disrupted education, compromised nutrition, child care issues and the financial costs to those families.
- Study Economy del’OS (OECD) studies show that school performance is critically dependent on maintaining close relationships with teachers.
- This is especially true for students from backward backgrounds who may lack the parental support they need to learn on their own.
- Working parents are more likely to lose their jobs when schools fail to take care of their children, which in many cases adversely affects wage losses and productivity.
- Localized school closures place a burden on schools as parents and authorities divert children to open schools.